| Home > Eclipses > Solar Eclipses > Five Millennium (-1999 to +3000) Canon of Solar Eclipses Database |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
During the 5,000-year period from -1999 to +3000 (2000 BCE to 3000 CE), Earth will experience 11,898 eclipses of the Sun. The statistical distribution of eclipse types for this interval is as follows : 4,200 partial eclipses, 3,956 annular eclipses, 3,173 total eclipses and 569 hybrid eclipses. All the data accessed through this interface is provided by Fred Espenak and Jean Meeus (NASA Technical Publication TP-2006-214141). The data available is described in greater detail in the Key to Solar Eclipse Catalogs. Years in this catalog are numbered astronomically and include the year 0. Historians should note there is a difference of one year between astronomical dates and BCE dates. Thus, the astronomical year 0 corresponds to 1 BCE, and astronomical year -1 corresponds to 2 BCE, etc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Xavier M. Jubier
1999 August 11
2001 June 21
2001 December 14
2002 December 4
2003 November 23
2005 April 8
2005 October 3
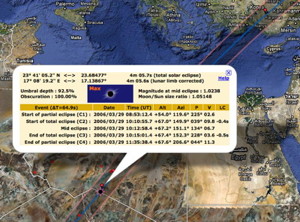
2006 March 29
2006 September 22
2008 February 7
2008 August 1st
2009 January 26
2009 July 22
2010 January 15
2010 July 11
2012 May 20
2012 November 14
2013 May 10
2013 November 3
2014 April 29
2015 March 20
2016 March 8-9
 Five Millennium (-1999 to +3000) Canon of Solar Eclipses Database
Five Millennium (-1999 to +3000) Canon of Solar Eclipses Database