E-Flight Module
The use of this module is strictly restricted and access is by invitation only. Proper authorization must be obtained in written from Xavier M. Jubier. Any unauthorized use is to be prosecuted and the user or those that benefited from this unauthorized use shall be liable. All commercial uses are subject to a fee for every planned flight.
Once you have unlocked the E-Flight module access with the provided instruction and identifiers, you’ll just have to open Solar Eclipse Maestro’s E-Flight Intercept Manager dialog.
-
Choose E-Flight > Shadow Intercept Manager…
For planning and execution purposes, the E-Flight module can be run asynchronously or synchronously in time; i.e., a flight plan can be developed and "simulated" without regard to the actual Coordinated Universal Time or rate of time-flow. The flight plan can be tested at a sped up or slowed down pace, and enabled for real-time use on-board the aircraft. In the latter case, the E-Flight module will synchronize to the computer’s internal clock and provide position/navigation information in real-time. -
Now you have to specify the eclipse flight parameters and either set the shadow intercept time or location.
These parameters will be used to develop a set of time-ordered waypoints which can then be loaded into an aircraft’s navigation/autopilot and/or FMS/FMC systems. The E-Flight module can re-compute a "corrected" flight plan in situ given changing wind conditions enroute to the eclipse intercept.
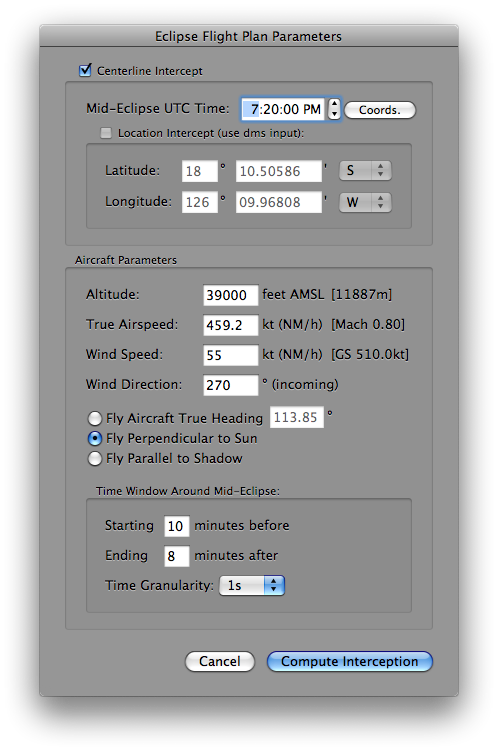
The following parameters must be provided:
- Centerline Intercept: specifies where the Moon’s shadow should be intercepted at mid-eclipse, either on the centerline or at another specific location. In the former case the intercept coordinates are computed from the mid-eclipse intercept time. In the latter case it is the mid-eclipse intercept time that is computed from the intercept coordinates.
- Mid-Eclipse UTC Time: specifies the Coordinated Universal Time (with one second granularity) at which the aircraft is to be concentrically located in the Moon’s shadow.
The Coords. button computes the centerline coordinates and solar circumstances at that time (should be used only after the flight altitude has been set) or the intercept time at a given location. - Altitude (between 0 and 500,000 feet): fixed altitude in feet of the aircraft above mean sea level.
- True Airspeed (between 0 and 10,000 knots): only the true air speed (not the ground speed, which will be compute based upon windage and course) should be given.
- Wind Speed (between 0 and 400 knots): specify the windspeed in knots (nautical miles per hour).
- Wind Direction: specify the direction where the wind is from in degrees east from true north.
- Flight Vector or True Aircraft Heading: true heading (i.e. geographic, not magnetic) should be given in degrees east of true north or one of the two other modes. The heading is the direction in which the longitudinal axis of the aircraft is pointing. Flying perpendicular to the Sun will present an optimized view of the eclipse from the aircraft, and will typically be necessary anywhere along the path except relatively near the points of local noon or midnight. Flying parallel to the shadow will maximize the duration of totality, but would likely not be practical near the beginning or end of the path.
- Time Window Around Mid-Eclipse: specifies how many minutes before and after mid-eclipse the aircraft is to fly on the to-be-computed "interception run". The time granularity at which the computations are displayed must be selected as well.
-
Once all the parameters have been entered you just need to click on the Compute Interception button. Computations are done with the utmost accuracy and lead to an in-flight eclipse duration accuracy of ±1 second.
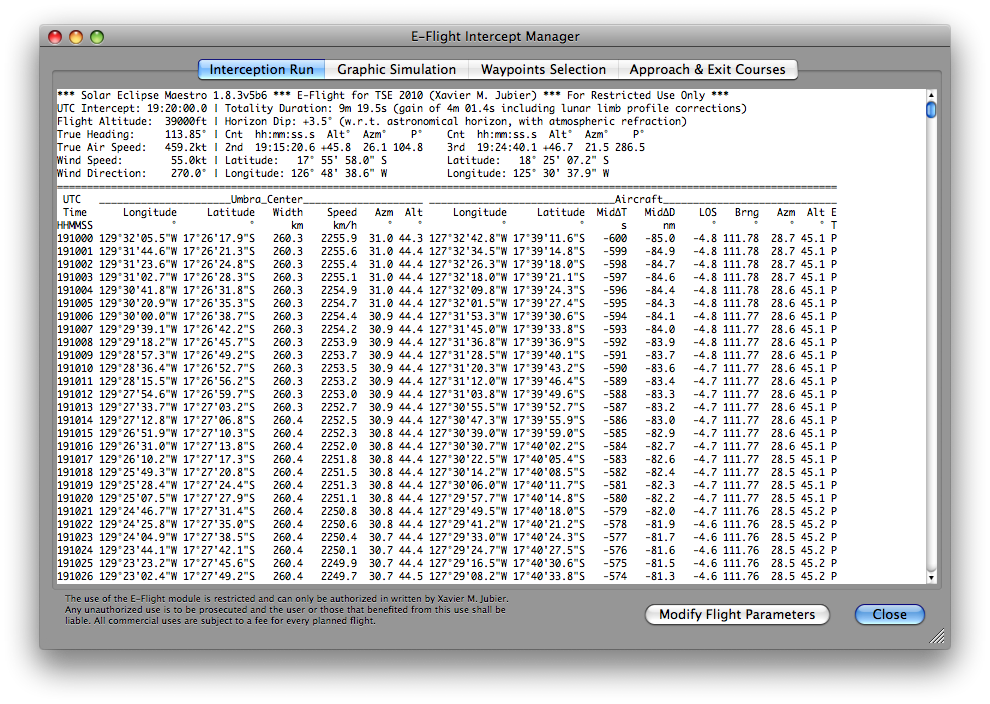
The text output is organized in three sections: a header, a table and a footer. The left side of the header region echoes back the input parameters from the Eclipse Flight Plan Parameters dialog. The right section provides the duration of totality or annularity and information on second and third contacts. The UTC time of each contact, along with the solar altitude, azimuth, and contact position angle is given, as is the location (latitude and longitude) of the aircraft at the instants of the contacts. The tabular section is presented in time order at the temporal resolution which was specified in the Eclipse Flight Plan Parameters dialog.
The time-ordered table section is as follows:
- UTC Time HHMMSS = Coordinated Universal Time (formatted as Hour, Minute, Second)
- Umbra Center Longitude = longitude of the center of the umbra
- Umbra Center Latitude = latitude of the center of the umbra
- Umbra Width = width of the umbral shadow projection in kilometers
- Umbra Speed = horizontal velocity of the umbral shadow projection in kilometers per hour
- Umbra Center Azimuth = azimuth of the Sun in degrees from that point
- Umbra Center Altitude = altitude of the Sun in degrees from that point
- Aircraft Longitude = longitude of the aircraft at the corresponding time
- Aircraft Latitude = latitude of the aircraft at the corresponding time
- MidΔT = Time in seconds until/since mid-eclipse
- MidΔD = Distance to be flown in nautical miles to/from mid-eclipse
- LOS = Line-of-Site horizontal deviation angle to the Sun w.r.t. aircraft windows in degrees
- Bearing = instantaneous bearing of the aircraft in degrees
- Aircraft Sun Azimuth = azimuth angle of the Sun from the aircraft in degrees
- Aircraft Sun Altitude = altitude of the Sun from the aircraft in degrees
- Eclipse Type = type of the eclipse from the aircraft (without any corrections applied)
-
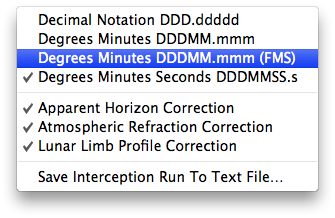
A contextual menu, that can be invoked with a right click over the tabulated data, will let you select various options:
- Decimal Notation DDD.ddddd - Display the aircraft coordinates in decimal notation
- Degrees Minutes DDDMM.mmm - Display the aircraft coordinates in degrees and minutes format
- Degrees Minutes DDDMM.mmm (FMS) - Display the aircraft coordinates in a Flight Management System (FMS) format
- Degrees Minutes Seconds DDDMMSS.s - Display the aircraft coordinates in degrees, minutes and seconds format
- Apparent Horizon Correction - Display the solar elevations with reference to the astronomical horizon and take into account the apparent horizon
- Atmospheric Refraction Correction - Take into account the atmospheric refraction or not
- Lunar Limb Profile Correction - Take into account the Kaguya lunar limb profile when computing the contact times or not
- Save Interception Run To Text File… - Allow the user to save the tabulated data to a text file
-
A clic on the Graphic Simulation tab enables you to view the relative positions and trajectories of the umbra and aircraft, as well as the direction of the Sun (yellow arrow when activated; the length and color of the arrow varies with the Sun’s elevation: the higher the Sun is the shorter the arrow, the lower the more orangish).
The display area is divided into a map region on the left and an information panel on the right. A time slider, visible only when the pointer hovers over the map, lets you choose the instants to view the simulation at. A live diagram of the eclipse as viewed from the aircraft can be seen in the lower right corner after resizing the window vertically.
While in-flight the live deviation from the planned course is also displayed when a GPS receiver (preferably a puck-like unit such as the Garmin GPS 18x USB) is connected to the Mac.
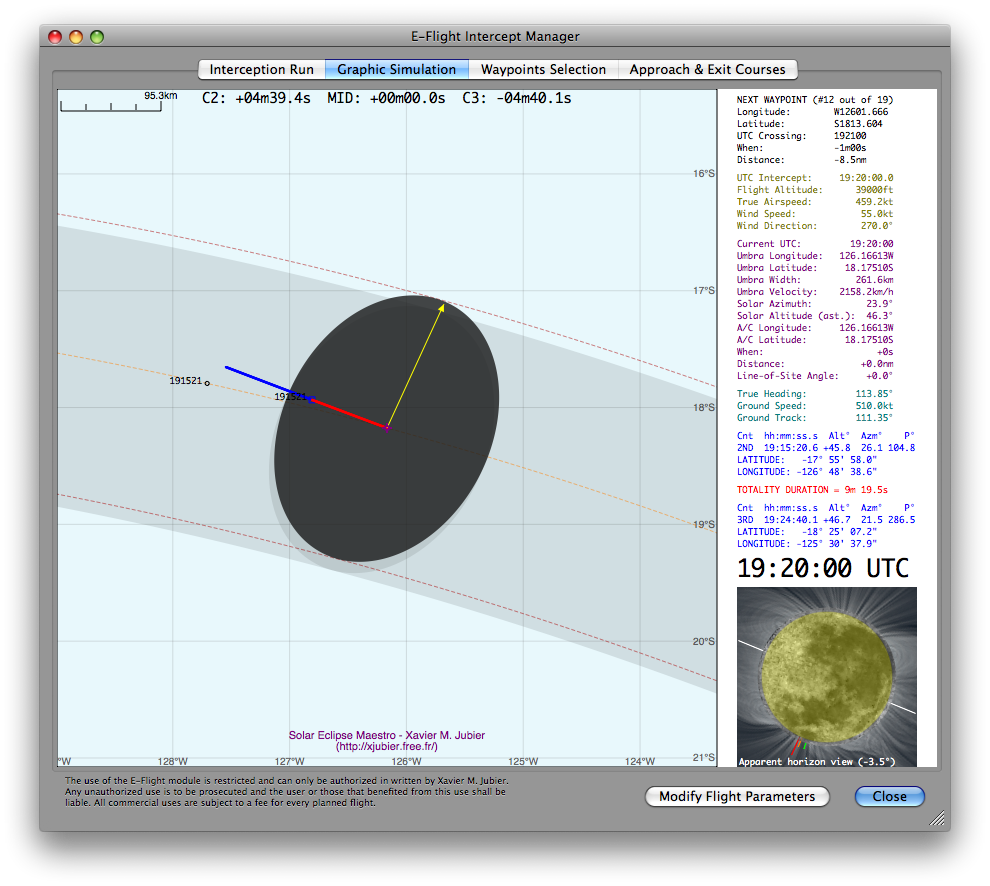
The map can be displayed in either equirectangular or stereographic projection, the latter being the best choice when looking at high latitudes (near the poles). The shaded umbral path is shown at sea level, while the dotted umbral path, umbral shadow and dotted centerline (in orange) are all displayed at the altitude of the aircraft.
The location of the point of mid-eclipse intercept is marked by a purple cross in the middle of the map.
The ground track of the aircraft is shown throughout the intercept phase. The positions before the aircraft enters the umbra (or, more generally as the umbra overtakes the aircraft [except in some circumstances for supersonic flight]) and after it exits the umbra (or after the umbra distances the aircraft) are marked in dark blue. Points along the ground track corresponding to times when the aircraft is flying through the umbral shadow are marked in red.
The instants and locations of second and third contact, marking the start and end of totality as seen from the moving aircraft, are annotated in black along the aircraft ground track as the aircraft passes those points. The locations are marked by small dark blue squares along with the Coordinated Universal Times (UTC) at which the contacts occur. In addition, the points along the centerline corresponding to the instants when the aircraft enters and exits the umbra are also annotated with the Coordinated Universal Times of those instants as small back circles.
The accuracy of contact times is more or less ±2 seconds: in fact many factors are affecting the error margin.
The information area on the right provides the eclipse circumstances and the aircraft flight parameters are updated at each incrementing time step. The eclipse as seen from the aircraft’s windows is displayed below at the current position. The information is presented in five (color coded) sections:
-
Next waypoint with both index and number of waypoints (in black)
Longitude = longitude of the next targeted waypoint
Latitude = latitude of the next targeted waypoint
UTC Crossing = UTC at which the aircraft will reach next waypoint
When = time remaining until next waypoint crossing
Distance = distance in nautical miles to next waypoint crossing -
Static Flight Parameters (in olive)
UTC Intercept = Coordinated Universal Time of mid-eclipse intercept
Flight Altitude = altitude of aircraft in feet
True Airspeed = true airspeed of aircraft in knots (nautical miles per hour)
Wind Speed = wind speed in knots (nautical miles per hour)
Wind Direction = incoming wind direction in degrees -
Dynamic Umbral Path and Aircraft Circumstances and Positions (in purple)
Current UTC = current Coordinated Universal Time
Umbra Longitude = longitude of the center of the umbra at flight altitude
Umbra Latitude = latitude of the center of the umbra at flight altitude
Umbra Width = width of the umbral shadow in kilometers at flight altitude
Umbra Velocity = instantaneous speed of the umbral shadow in kilometers per hour
Solar Azimuth = solar azimuth from the aircraft at current UTC in degrees east of true north
Solar Altitude = solar elevation from the aircraft at current UTC in degrees with reference to the astronomical horizon
A/C Longitude = longitude of aircraft
A/C Latitude = latitude of aircraft
When = time to/from mid-eclipse intercept
Distance = flight distance in nautical miles to/from mid-eclipse intercept
Line-of-Site Angle = horizontal deviation in degrees from line-of-site viewing angle to Sun orthogonal to direction of aircraft -
Dynamic/Static Instantaneous Flight Vector (in light sea green)
True Heading = true heading of aircraft in degrees east of true north (direction in which the longitudinal axis of the aircraft is pointing)
Ground Speed = ground speed of aircraft in knots (nautical miles per hour)
Ground Track = ground track direction in degrees east of true north -
Static Contact Information (in dark blue and red)
Coordinated Universal Time of second and third contacts
Solar elevation in degrees with reference to the astronomical horizon at contacts
Solar azimuth in degrees east of true north at contacts
Position angles of contacts along solar limb in degrees east from north
Aircraft position (latitude and longitude) at contact times
Duration of totality or annularity in minutes and seconds
-
Next waypoint with both index and number of waypoints (in black)
-
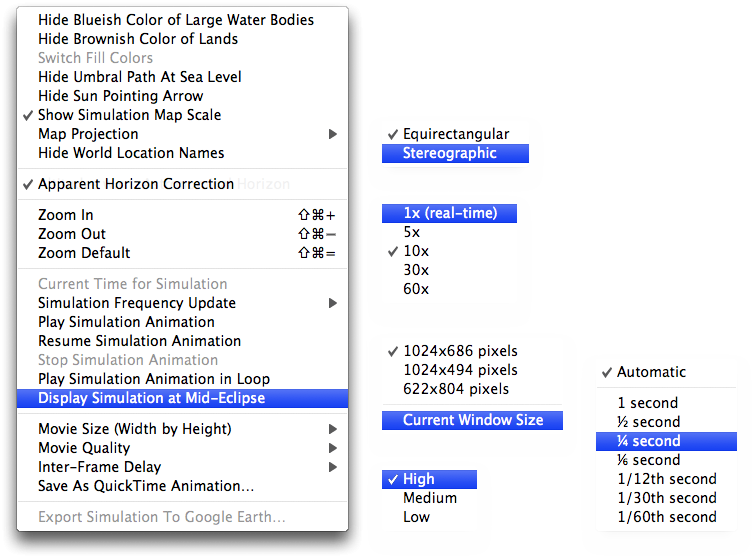
A contextual menu, that can be invoked with a right click over the map, will let you select various options:
- Hide Blueish Color of Large Water Bodies - Display or hide the blue color of large water bodies (seas, lakes, etc.)
- Hide Brownish Color of Lands - Display or hide the brown color of lands above sea level (continents, islands, etc.)
- Switch Fill Colors - In stereographic projection to allow switching the fill colors used for the sea and land
- Hide Umbral Path At Sea Level - Display or hide the shaded (ant-)umbral path at sea level
- Show Umbra At Sea Level - Display or hide the (ant-)umbra at sea level
- Hide Sun Pointing Arrow - Display or hide the direction of the Sun
- Show Visibility Ground Range - Display or hide the visibility range to the ground from the aircraft in yellow
- Show Visibility Cloud Tops Range - Display or hide the visibility range to the cloud tops at about 30,000 feet from the aircraft in orange
- Show Simulation Map Scale - Display or hide the scale on the simulation map (available only for the equirectangular projection)
-
Map Projection
- Equirectangular - Recommended but near the poles
- Stereographic - Best used at high latitudes close to the poles
- Center on Mid-Eclipse Intercept Location - When deactivated the map is centered midway between the flight departure airport, if defined, and the mid-eclipse intercept location
- Hide World Location Names - Display or hide the world locations overlaid on the map
- Show Only Main Cities - Display only the major cities overlaid on the map
- Show NASA Blue Marble Earth Imagery - Use or not the NASA Blue Marble Earth as the background. Monthly images are used when possible. An opacity slider is activated so you can control the opacity of the satellite imagery.
- Apparent Horizon Correction - Display the solar elevations with reference to the astronomical horizon taking into account the apparent horizon and draw the Sun-Moon diagram accordingly
- Zoom In (⌘⇪+) - Zoom in one level
- Zoom Out (⌘⇪-) - Zoom out one level
- Zoom Default (⌘⇪=) - Zoom to the default value
- Current Time for Simulation - Enabled only when the current system time is in use, which generally means in-flight. This option lets you synchronize the simulation with the real flight when there is no GPS position tracking.
-
Simulation Frequency Update
- 1x (real-time) - The simulation is updated in real-time every second
- 5x - The simulation is updated every 5 seconds
- 10x - The simulation is updated every 10 seconds
- 30x - The simulation is updated every 30 seconds
- 60x - The simulation is updated every 60 seconds
- Play Simulation Animation - Start playing the simulation (enabled only when there is no GPS position tracking)
- Resume Simulation Animation - Resume the simulation previously stopped (enabled only when there is no GPS position tracking)
- Stop Simulation Animation - Stop playing the simulation (enabled only when there is no GPS position tracking)
- Play Simulation Animation in Loop - Set to play the simulation in loop
- Display Simulation at Mid-Eclipse - Display the simulation at the time of mid-eclipse (enabled only when there is no GPS position tracking)
-
Movie Size (Width by Height)
- 3840x2160 pixels (4K) - 4K size in landscape format with the Sun-Moon diagram
- 1920x1080 pixels (HD) - Full HD size in landscape format with the Sun-Moon diagram
- 1280x720 pixels - Full size in landscape format with the Sun-Moon diagram
- 1024x686 pixels - Full size in landscape format with the Sun-Moon diagram
- 1024x494 pixels - Reduced size in landscape format without the Sun-Moon diagram
- 622x804 pixels - Full size in portrait format with the Sun-Moon diagram
- Current Window Size - Use the current window size
-
Movie Quality
- High - Full resolution and no compression
- Medium - Full resolution with compression
- Low - Full resolution with reduced number of colors and compression
-
Inter-Frame Delay
- Automatic - The best value is automatically selected
- 1 second - One second between each image
- ½ second - Half a second between each image
- ¼ second - One fourth of a second between each image
- ⅙ second - One sixth of a second between each image
- 1/12th second - One twelfth of a second between each image
- 1/30th second - One thirtieth of a second between each image
- 1/60th second - One sixtieth of a second between each image
- Save As QuickTime Animation… - Allow the user to save the simulation as a QuickTime movie
- Export Simulation To Google Earth… - Allow the user to visualize the simulation in Google Earth
-
A clic on the Waypoints Selection tab enables you to view and manage the series of time correlated waypoints.
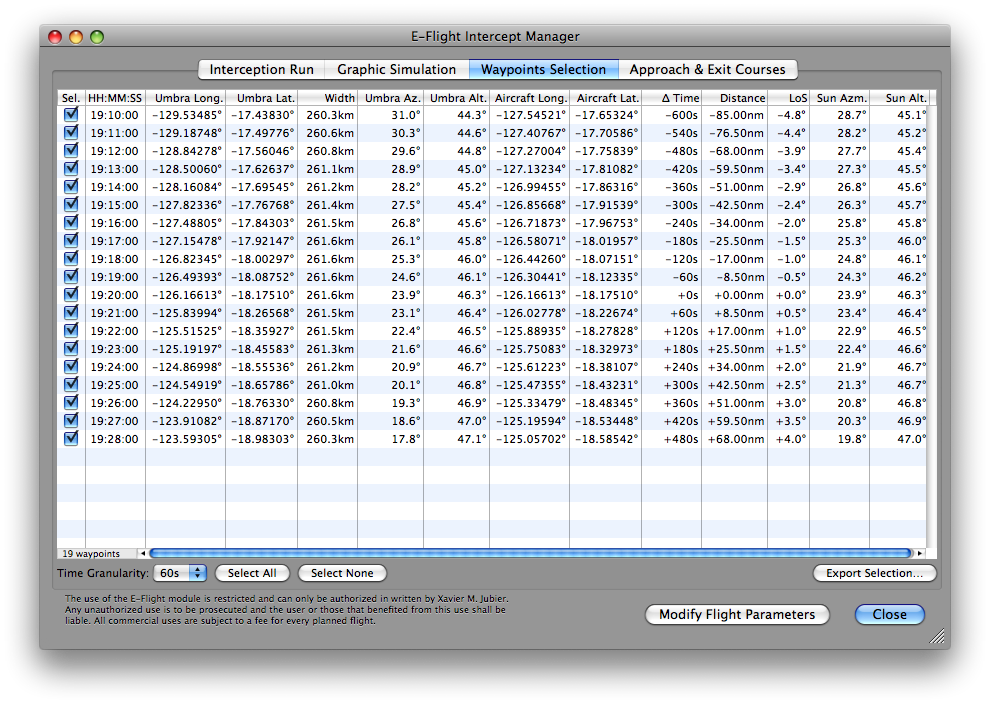
They all don’t need to be selected, but the one at mid-eclipse is always selected.
A totality or annularity run is defined by a series of time correlated waypoints to which the aircraft trajectory must conform both in position and time. The trajectory may be very closely approximated, by extracting a discrete set of waypoints from the more densely computed values. For nearly all eclipses (except for those where the width of the shadow is extremely small, and also the ones very close to the points of sunrise or sunset) waypoint densities on the order of several minutes in time will not limit the accuracy achieved in the actual targeting of the aircraft. -
A contextual menu, that can be invoked with a right click over the waypoints databrowser, will let you choose among various items:
- Select All Interception Run Waypoints - To select all the waypoints at once
- Deselect All Interception Run Waypoints - To deselect all the waypoints, but the mid-eclipse, at once
- Save Interception Run Selected Waypoints To Text File… - Allow the user to save the selected waypoints to a text file
- Export Interception Run Selected Waypoints To Google Earth… - Allow the user to create a Google Earth file with the selected waypoints
-
A clic on the Approach & Exit Courses tab enables you to compute the approach course needed to reach the beginning of the eclipse intercept trajectory.
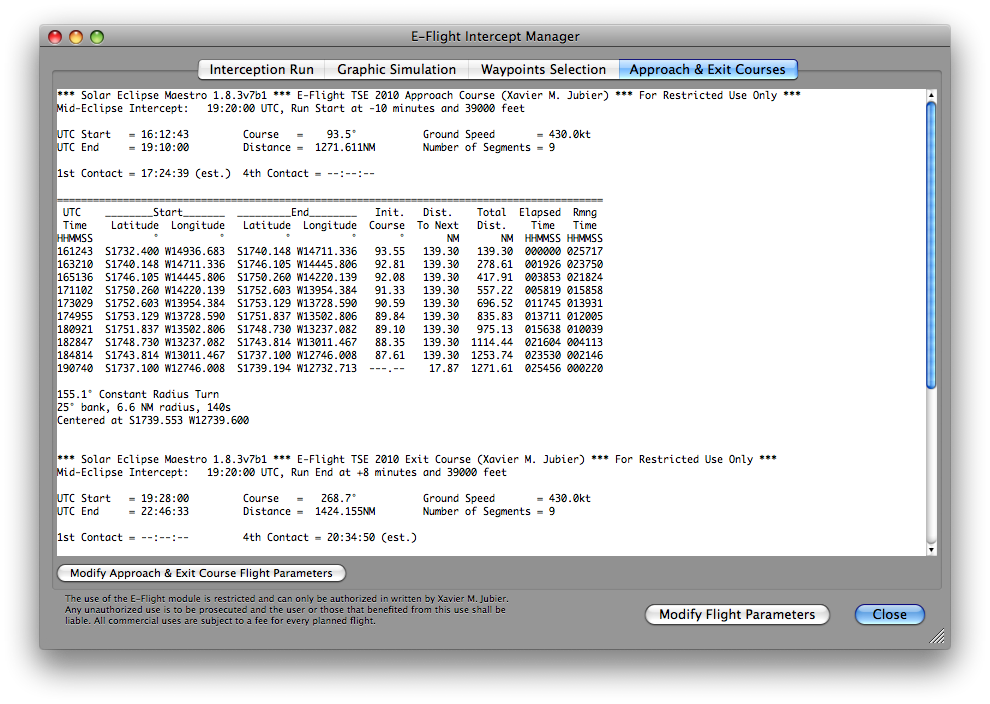
-
Now you can specify the approach course parameters from your departure location to reach the eclipse intercept trajectory. An exit course is also generated at the end of the eclipse intercept trajectory.
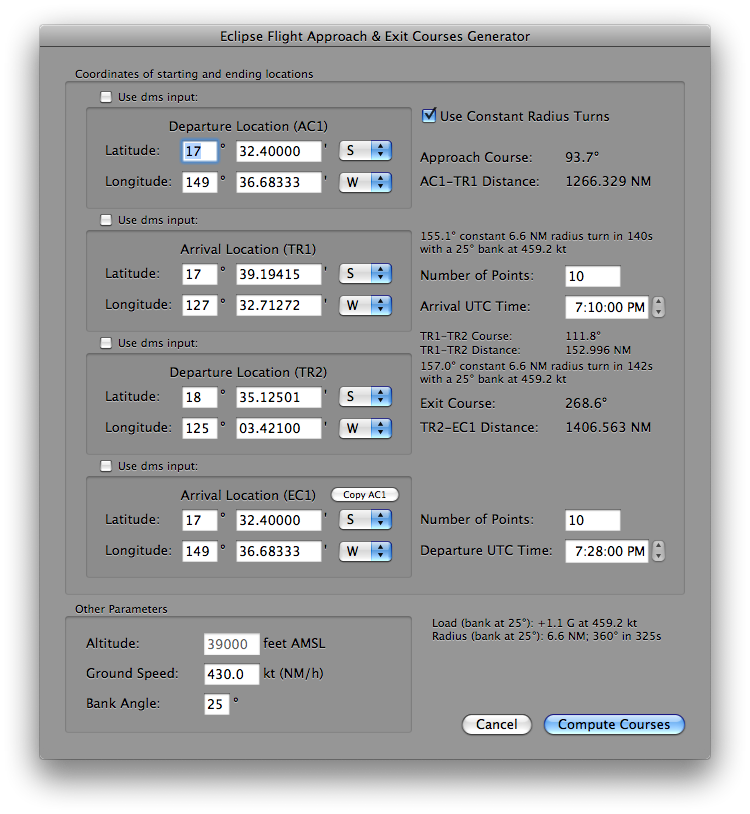
-
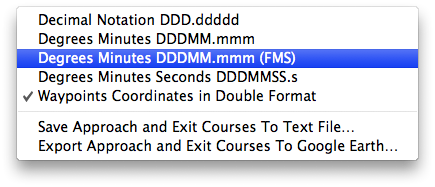
A contextual menu, that can be invoked with a right click over the tabulated approach and exit courses, will let you choose among various items:
- Decimal Notation DDD.ddddd - Display the aircraft coordinates in decimal notation
- Degrees Minutes DDDMM.mmm - Display the aircraft coordinates in degrees and minutes format
- Degrees Minutes DDDMM.mmm (FMS) - Display the aircraft coordinates in a Flight Management System (FMS) format
- Degrees Minutes Seconds DDDMMSS.s - Display the aircraft coordinates in degrees, minutes and seconds format
- Waypoints Coordinates in Double Format - Display the aircraft coordinates in degrees and minutes format and in decimal format as well
- Save Approach and Exit Courses To Text File… - Allow the user to save the approach and exit courses waypoints to a text file
- Export Approach and Exit Courses To Google Earth… - Allow the user to create a Google Earth file with the approach and exit courses waypoints
Only the total and annular eclipses, hence the hybrids as well, are handled.
Additional overlays can be provided by putting them directly in the following user folder:
~/Library/Application Support/SolarEclipseMaestro/AdditionalOverlays/
That folder is created automatically by Solar Eclipse Maestro and can be opened directly by selecting the corresponding item in the Window menu.
To have the additional overlays available for every user, put them directly in the following folder:
/Library/Application Support/SolarEclipseMaestro/AdditionalOverlays/
Glenn Schneider’s E-Flight application inspired some of my work on Solar Eclipse Maestro’s E-Flight module although it shares only a somewhat similar user interface.